Glycerine – The Skincare Essential You Didn’t Know You Need)
Ever wondered why glycerine is present in almost every moisturizer and serum? While skincare trends constantly change, glycerine remains a staple ingredient, praised for its hydrating and skin-repairing properties. But is glycerine in skincare it truly essential, or is its effectiveness overhyped?
Often overshadowed by trendy ingredients like hyaluronic acid, glycerine is one of the most scientifically proven and dermatologist-recommended humectants. Whether you have dry, oily, or sensitive skin, glycerine should be a staple in your skincare routine.
So, what makes glycerine in skincare so powerful? Let’s break it down.
- Glycerine – The Skincare Essential You Didn’t Know You Need)
- What is Glycerine?
- How Does Glycerine in Skincare Work?
- Glycerine in Skincare vs. Other Humectants: Which One is Best for You?
- Glycerine in Skincare: Anti-Aging and Skin Repair
- Glycerine as an Anti-Pollution Shield
- Is Glycerine Safe for Sensitive Skin?
- Can Glycerine in Skincare Have Negative Effects?
- Glycerine in Skincare: Should You Use It?
- Final Thoughts: Why Glycerine in Skincare Remains a Essential

What is Glycerine?
Glycerine, or glycerol, is a naturally occurring sugar alcohol (polyol) that attracts moisture to the skin. It’s a byproduct of fat metabolism in plants and animals and can also be synthesized from petroleum-derived sources. In cosmetics, glycerine is valued for its humectant properties, meaning it draws water from both the environment and deeper skin layers to keep the skin hydrated and supple.
It is a small molecule—sticky, syrupy, and sweet—with a grand purpose: it attracts water and hydrates the skin.
How Glycerine is Produced
There are two main ways glycerine is obtained:
- Plant-Based Extraction: A byproduct of saponification (soap-making) or biodiesel production. It’s commonly derived from coconut, palm, or soybean oil.
- Synthetic Production: Manufactured from petrochemical processes, though molecularly identical to natural glycerin.
Its eco-friendliness and sustainability depend on the source. Plant-derived glycerine is generally preferred for clean beauty formulations, while synthetic glycerine is often found in industrial applications due to cost-effectiveness.

At its core, glycerine is a water magnet.
How Does Glycerine in Skincare Work?
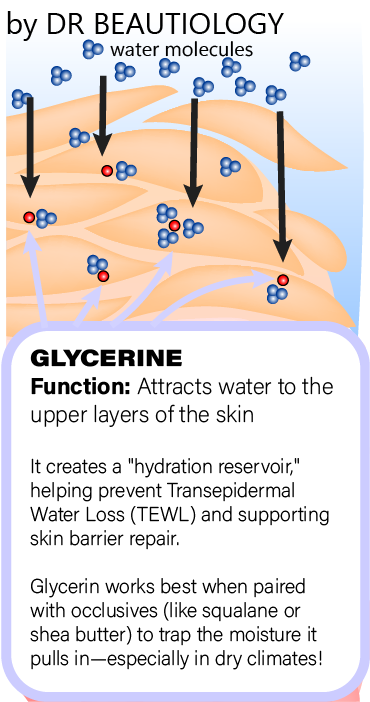
At its core, glycerine is a water magnet. As a humectant, it pulls moisture into the skin and retains it within the stratum corneum (outermost skin layer). But its benefits extend beyond hydration.
Humectant Action: Deep Hydration & Moisture Retention
Unlike other humectants, glycerine doesn’t just sit on the surface—it penetrates into the skin, enhancing hydration at multiple levels. It actively binds to water molecules, creating a reservoir of hydration that prevents transepidermal water loss (TEWL). This helps maintain a healthy moisture balance, reducing dryness and flakiness.
Studies show that glycerine binds and holds onto water more effectively than many other humectants, including propylene glycol and sorbitol.
Strengthening the Skin Barrier
A well-hydrated skin barrier is essential for protection against pollutants, irritants, and allergens. Studies have shown that glycerine plays a role in repairing the skin barrier.
Fun Fact: Creams with glycerine improve skin barrier recovery after irritation caused by harsh soaps (like sodium laureth sulfate, SLS)!
Enhancing the Absorption of Other Ingredients
Glycerine isn’t just a hydrator—it also enhances the bioavailability of active ingredients. According to a study published in Molecules, glycerin-based nano-emulsions significantly improve the absorption of both hydrophilic and lipophilic compounds. This means that when paired with antioxidants, peptides, or ceramides, glycerine can increase their effectiveness, making it a great carrier ingredient in serums and treatments.

When paired with antioxidants, peptides, or ceramides, glycerine can increase their effectiveness, making it a great carrier ingredient in serums and treatments.
Glycerine in Skincare vs. Other Humectants: Which One is Best for You?
While glycerine is widely regarded as the gold standard humectant, it’s not the only option. Other hydrating ingredients, such as hyaluronic acid, urea, sodium PCA, and propylene glycol, work in different ways. Below is a comparison to help you choose the best fit for your skin type.
| Humectant | Source | Function | Pros | Cons |
| Glycerine | Plant-based or synthetic | Draws water into skin | Deep hydration, enhances absorption of actives, non-irritating | Can feel sticky at high concentrations |
| Hyaluronic Acid | Fermentation or synthetic | Holds water at surface | Plumps skin, works well in serums | Large molecules may not penetrate deeply, expensive in high-quality forms |
| Urea | Natural (found in skin’s NMF) | Hydrates + exfoliates | Softens rough skin, promotes cell turnover | High % can cause irritation |
| Sodium PCA | Derived from amino acids | Retains moisture | Lightweight, good for oily skin | Less potent than glycerine in low humidity |
| Propylene Glycol | Synthetic | Enhances penetration | Helps actives absorb deeper | May cause irritation in sensitive skin |
| Sorbitol | Plant-derived | Binds water to skin | Non-irritating, good for sensitive skin | Less effective than glycerine in dry climates |
Key Takeaways:
- Glycerine vs. Hyaluronic Acid: Glycerine penetrates deeper, while HA holds water on the skin’s surface.
- Glycerine vs. Urea: Urea hydrates and exfoliates, making it ideal for rough, aging skin.
- Glycerine vs. Sodium PCA: Sodium PCA is lighter and better for oily skin, but less hydrating overall.
- Glycerine vs. Propylene Glycol: Glycerine is better tolerated, while PG enhances penetration but can be irritating.
Best for:
- Dry, dehydrated skin: Glycerine + Hyaluronic Acid
- Oily, acne-prone skin: Sodium PCA or lightweight HA
- Aging, rough skin: Urea + Glycerin
- Sensitive skin: Glycerine + Sorbitol

Glycerine is a powerful moisture-binding ingredient that not only hydrates the skin but also supports anti-aging and repair mechanisms at a cellular level.
Glycerine in Skincare: Anti-Aging and Skin Repair
Aging affects the skin in many ways—moisture levels drop, collagen production slows, and the skin barrier weakens. This results in dryness, fine lines, and increased sensitivity. Glycerine is a powerful moisture-binding ingredient that not only hydrates the skin but also supports anti-aging and repair mechanisms at a cellular level.
How Glycerine Plumps and Firms the Skin
One of the key signs of youthful skin is its ability to retain moisture. As we age, the Natural Moisturizing Factors (NMFs) in our skin deplete, leading to a dull, sagging appearance. Glycerine acts as a moisture reservoir, ensuring that hydration is maintained at multiple skin layers.
Glycerine enhances skin elasticity by improving the function of aquaporins—proteins that help transport water within skin cells. This results in better skin flexibility and fewer visible fine lines.
Supporting Skin Cell Regeneration and Repair
Our skin naturally sheds and renews itself every 28 to 40 days, but this process slows down with age or due to environmental damage. When hydration is lacking, dead skin cells accumulate, making the skin appear rough and uneven.
Glycerine helps by:
- Increasing epidermal hydration, ensuring optimal cell turnover.
- Strengthening the skin’s natural lipid matrix, therefore ensuring a resilient and well-hydrated barrier for lasting moisture and protection.
- Reducing inflammation, making it beneficial for post-procedure skin healing.
For individuals undergoing treatments such as chemical peels, laser therapy, or microneedling, glycerin-based formulations can accelerate recovery and reduce irritation.
Glycerine as an Anti-Pollution Shield
Pollution and free radicals contribute to premature aging by breaking down collagen and damaging skin cells. While glycerine itself is not an antioxidant, studies show that it enhances the delivery of antioxidants like Vitamin C and green tea extract, ensuring deeper absorption.
By acting as a carrier for these protective ingredients, glycerine helps neutralize oxidative stress and reinforce the skin barrier, making it a valuable component of anti-aging skincare routines.

While not an antioxidant itself, glycerine boosts the absorption of antioxidants like vitamin C and green tea extract.
Is Glycerine Safe for Sensitive Skin?
For those with sensitive or compromised skin, glycerine is often a recommended ingredient due to its ability to restore skin barrier function and prevent water loss.
Calming Redness and Irritation
Unlike certain humectants that can over-exfoliate or irritate the skin, glycerine has a soothing effect. Research published in Medicina found that glycerin-based moisturizers improved hydration in patients with atopic dermatitis, significantly reducing flare-ups and discomfort.
Glycerin’s non-reactive and hypoallergenic nature makes it ideal for:
- Eczema-prone skin – Prevents itchiness and dryness.
- Rosacea skin – Reduces irritation and redness.
- Post-inflammatory skin – Speeds up healing after acne breakouts.
Does Glycerine Cause Acne?
There is a myth that glycerine clogs pores and causes breakouts, but the reality is different. Glycerine is non-comedogenic, meaning it does not block pores. In fact, for individuals with acne-prone skin, hydration is crucial to prevent the overproduction of sebum.
Dry skin often triggers compensatory oil production, leading to breakouts. By balancing moisture levels, glycerine can reduce excessive oiliness and promote faster healing of acne scars.
Glycerine for Post-Treatment Skin Recovery
For individuals recovering from chemical peels, laser treatments, or exfoliation, glycerin-based serums and creams provide instant relief. Research indicates that glycerine enhances epidermal regeneration, reducing post-procedure dryness and sensitization.
✔ Use a glycerin-rich barrier cream after treatments to lock in hydration.
✔ Look for fragrance-free formulations to avoid additional irritation.
Can Glycerine in Skincare Have Negative Effects?
While glycerine is generally safe for all skin types, improper use or overuse can sometimes lead to unintended drawbacks.
Can Glycerine Dry Out Your Skin?
Ironically, in extremely dry climates where there is little humidity in the air, glycerine can start pulling moisture from deeper skin layers instead of the environment, potentially leading to dehydration.
How to Avoid This:
✔ Always combine glycerine with occlusive agents (like shea butter or squalane) to seal in moisture.
✔ Use a humidifier indoors if you live in a dry climate.
Sticky or Heavy Texture at High Concentrations
Glycerine is best used in 5-10% concentrations in skincare formulations. When present in excess, it can feel sticky, tacky, or heavy, making it less ideal for daytime use under makeup.
How to Avoid This:
✔ Opt for lightweight glycerine serums instead of thick creams.
✔ Use glycerine at night if you dislike its slightly dewy finish.
Can Some People Be Sensitive to Glycerin?
Although rare, some individuals may experience mild irritation with undiluted glycerine or highly concentrated formulas. If irritation occurs:
✔ Conduct a patch test before using a new product.
✔ Pair glycerine with soothing ingredients like aloe vera or ceramides.
Glycerine in Skincare: Should You Use It?
Who Should Use Glycerin?
- Dry or Dehydrated Skin – Restores hydration and plumps skin.
- Aging Skin – Softens fine lines and supports collagen production.
- Sensitive Skin – Repairs the barrier and reduces irritation.
- Oily/Acne-Prone Skin – Hydrates without clogging pores.
- Post-Treatment Skin – Aids in healing and reduces inflammation.
Who Should Be Cautious?
- Those in Low-Humidity Areas – Should combine glycerine with occlusives.
- Individuals with Extremely Oily Skin – Can opt for lighter humectants like sodium PCA.
- Those with Allergies to Sugar Alcohols – Although rare, sensitivity to glycerine may occur.
Glycerine in Dermatological and Medical Skincare
Glycerine is not just a cosmetic ingredient; its use in dermatological treatments and medical-grade skincare is rapidly expanding:
- Post-procedure recovery: Glycerin-based creams and serums are used for soothing and protecting skin after laser treatments, chemical peels, and micro-needling.
- Barrier repair therapy: Glycerine is a core ingredient in prescription-grade moisturizers formulated for chronic skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and rosacea.
- Wound healing applications: New research is exploring glycerin-infused bandages that support faster tissue regeneration and improved hydration for wound care.
As skincare merges with medical science, glycerin’s role will continue to expand in functional and therapeutic skincare solutions.

Glycerine remains one of the most versatile, effective, and sustainable ingredients for skincare
Final Thoughts: Why Glycerine in Skincare Remains a Essential
As the skincare industry evolves, glycerine remains one of the most versatile, effective, and sustainable ingredients available. Whether used in traditional hydration serums or cutting-edge skincare technologies, it continues to be a must-have for healthy, well-hydrated skin.
Key Takeaways:
- Glycerine is biodegradable, renewable, and a sustainable choice in eco-conscious skincare.
- Encapsulation, hydrogels, and hybrid formulations are advancing glycerin’s effectiveness.
- Transparency in formulations and clean beauty marketing are making glycerine even more popular.
- Personalized skincare innovations are incorporating glycerine into custom hydration solutions.
- Medical and therapeutic skincare uses glycerine for wound healing, barrier repair, and post-procedure recovery.
Whether you prefer classic glycerin-based moisturizers or high-tech skincare innovations, this powerful ingredient will continue to define the future of hydration and skin barrier care.
Join the Conversation!
Do you use glycerine in your skincare routine? What do you think about the future of glycerin-based skincare? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
Talk to you soon!
Dr. Bozica
References:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31840548/
https://www.medicaljournals.se/acta/content/html/10.2340/00015555-2493
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/24/24/17335
https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9284/9/3/61
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/22/16/8749
https://www.mdpi.com/1648-9144/58/7/888
Is it better to use glycerine on damp skin, or does it still work the same on dry skin?
It is better to use it on damp skin, as it can pull water from the skin surface
Such a great deep dive 👏 I’ve definitely been overlooking glycerine. Adding it to my winter routine ASAP.
wow had no clue glycerin was that important lol. i always thought it was just there to make stuff feel smooth 😅 def gonna look out for it now
Honestly, I didn’t even realize glycerol and glycerin were the same thing 😅. This was super helpful, thank you!